Most people don’t watch corporate training videos — or, in cases where the training’s mandatory, don’t give them their full attention. According to a recent poll from Kaltura, the video tech provider, 75% of staffers admit to skimming through training videos, watching them without sound or listening to them while multitasking.
So, given that training videos aren’t cheap to produce, is there a way to make them more engaging and thus less of a money sink? Dominik Mate Kovacs, the co-founder and CEO of Colossyan, thinks there is — and it involves GenAI.
Colossyan taps AI to generate workplace learning videos, remixing, re-animating and editing footage of one of several virtual avatars against changeable backdrops. Users can enter a script to have it “read” aloud by Colossyan’s text-to-speech (TTS) engine, which also translates the script into over 70 languages.
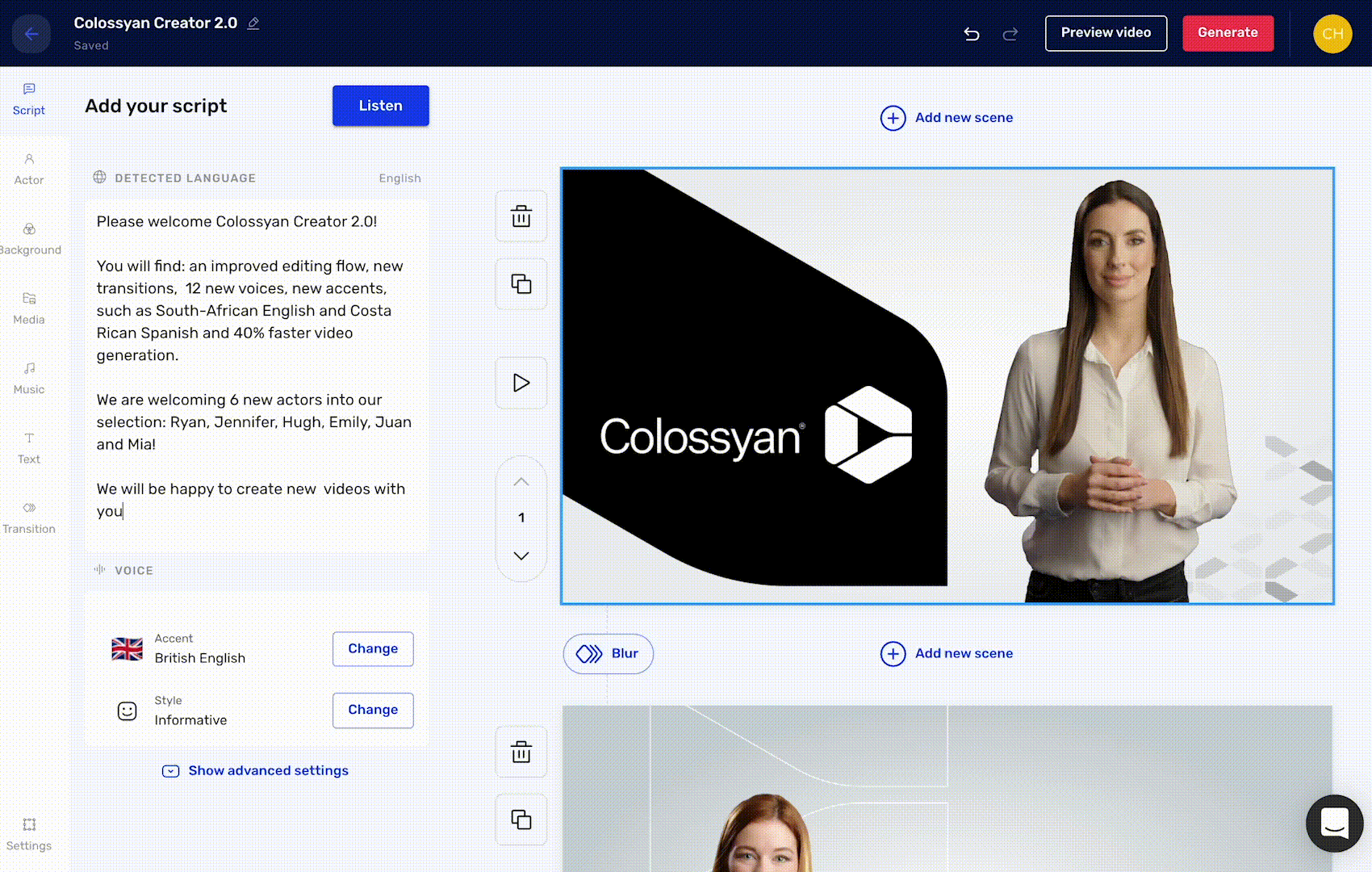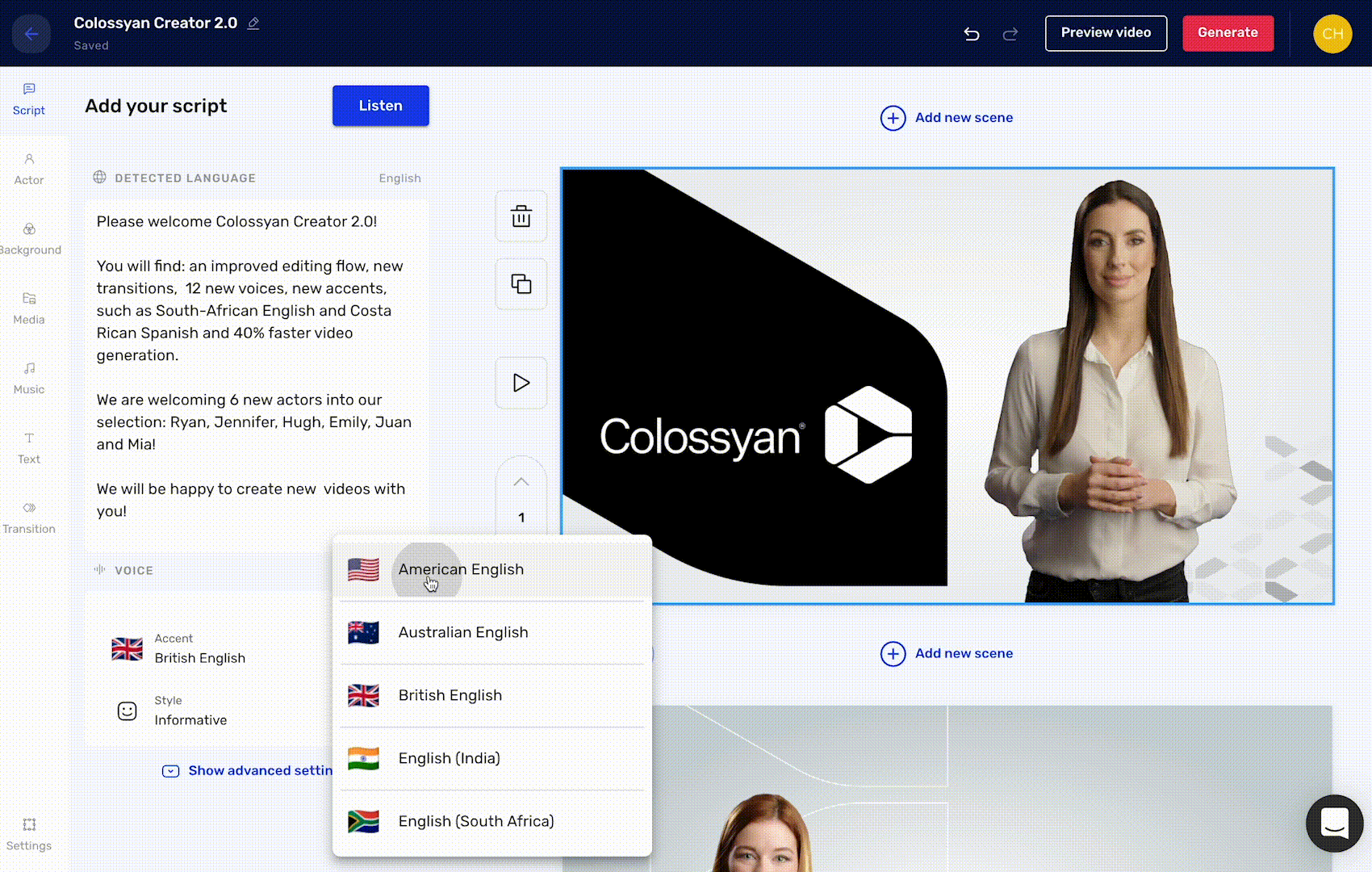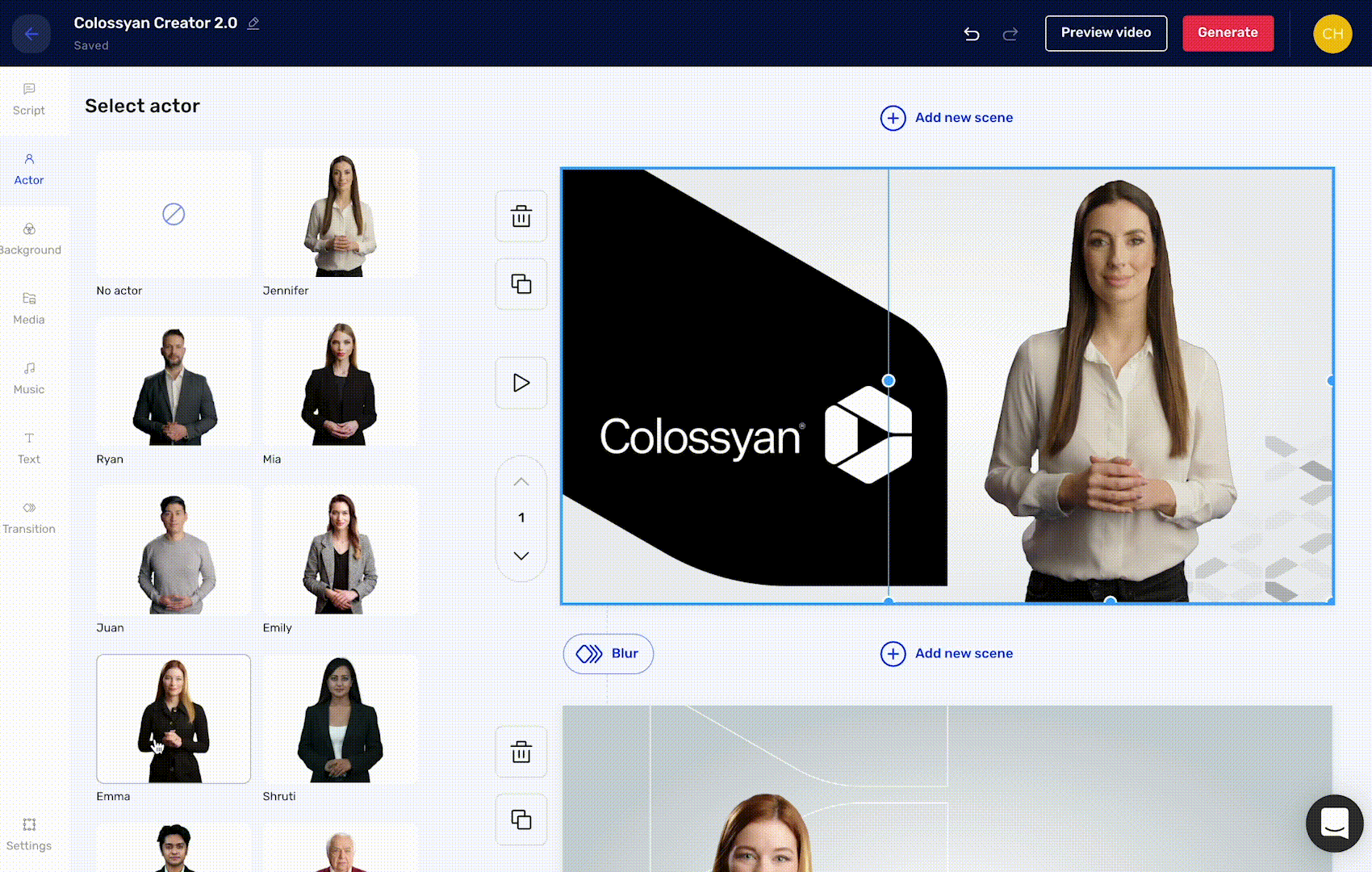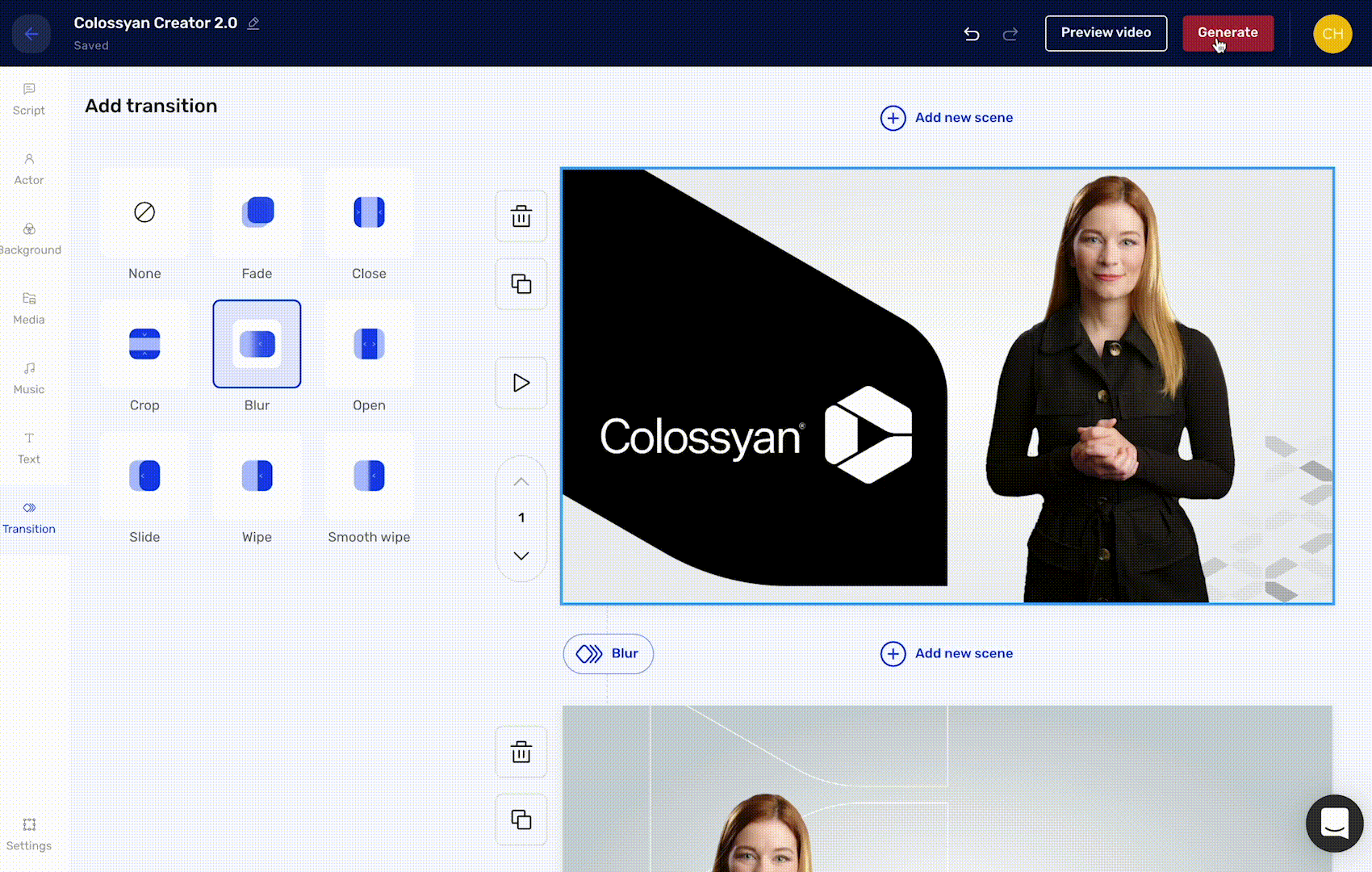
Image Credits: Colossyan
“To generate a video with Colossyan’s AI video platform, all you have to do is input a script and select from a diverse range of avatars,” Kovacs told TechCrunch in an email interview. “Any company can create a video about almost anything efficiently, without the need for conventional filming resources.”
Kovacs founded Colossyan in 2020 after leaving Defudger, a deepfakes detection platform, which he helped to co-launch. An engineer and data scientist by training, Kovacs says that he was inspired to start Colossyan by the budding corporate interest in GenAI.
“Enterprises are leveraging AI in diverse areas such as IT automation, customer care and digital labor — highlighting the broad applicability and potential impact of AI technologies in streamlining operations and enhancing service delivery,” Kovacs said. “The barriers to AI adoption, such as limited AI skills and data complexity, are significant yet surmountable challenges that many organizations are actively working to overcome. ”
For the heck of it, I gave Colossyan’s platform, which offers a free trial, a go to see if I could make a training video that’d successfully hold the attention of my ADHD brain — admittedly a high bar. The avatars were a bit too stiff and cartoonish for my liking and the TTS engine too robotic, at least compared to some of the more sophisticated GenAI tools out there (e.g. ElevenLabs). But I’ve certainly seen worse corporate videos.
Colossyan also doesn’t generate videos as quickly as I’d expect — a 38-second clip takes ~11 minutes. Granted, that’s a lot faster than creating trainings from scratch. But frankly, faced with the prospect of generating more than a handful of videos for whatever purpose, I’d be tempted to go the PowerPoint or Canva route instead.
I’m not Colossyan’s target market, of course. And it seems that several household brands are happy to pay for a subscription to Colossyan as it exists today, including Novartis, Porsche, Vodafone, HPE and Paramount, claims Kovacs.
Kovacs attributes the customer traction to features like integrations with learning management systems and a “conversation mode’ that allows two avatars to hold a dialogue with each other. He doesn’t deny that there’s a fair amount of competition in the GenAI video space — see CommonGround, Synthesia and Surge plus solutions from tech giants like Microsoft — but he thinks that Colossyan’s focus on “interactivity and engagement,” as he puts it, will continue to set the platform apart.
Perhaps he’s right. Colossyan today announced that it raised $22 million in a funding round led by Lakestar with participation from Launchub, Day One Capital and Emerge Education. The proceeds will be put toward tripling Colossyan’s headcount across its New York, London and Budapest offices, Kovacs says, and developing new capabilities like branching videos and knowledge checks.
“For C-suite and IT department leaders, our platform represents a scalable, cost-efficient solution to training and development challenges,” he added.









