A fledgling startup founded by one of OpenAI’s first engineering hires is looking to “redefine manufacturing,” with AI-powered factories for creating bespoke precision parts.
Daedalus, as the company is called, is based in the southwestern German city of Karlsruhe, where its solo factory is currently housed. Here, Daedalus takes orders from industries such as medical devices, aerospace, defence, and semiconductors, each requiring unique components for their products. For example, a pharmaceutical company might require a customized metal casing for a valve used in the production of a particular medicine.
As it looks to ramp up operations with a view toward opening additional factories in its domestic market, Daedalus today announced it has raised $21 million in a Series A round of funding led by Nokia-funded NGP Capital, with participation from existing investors Khosla Ventures and Addition.
This takes Daedalus’s total funding past the $40 million mark, with other notable investors including Y Combinator (YC) which became involved after Daedalus participated in YC’s Winter 2020 program.
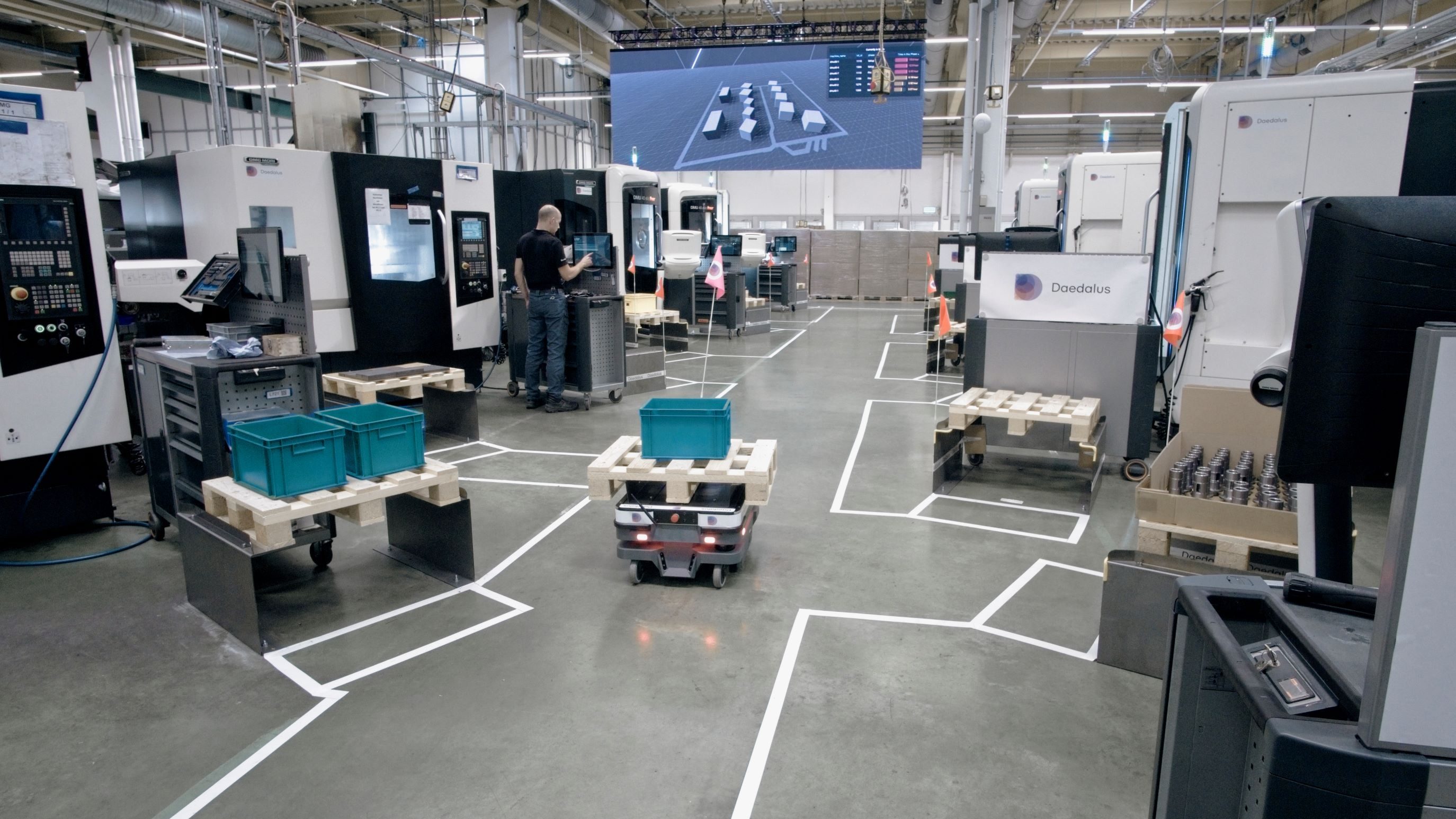

The Daedalus factory floor Image Credits: Daedalus
Fragmented fabrication
The manufacturing industry — particularly as it relates to precision part fabrication — is hugely fragmented by just about every estimation. While it’s tempting to imagine that a typical manufacturing setup in 2024 is something akin to that of a large automotive assembly plant, this really only applies where high-volume products (like cars) are involved — the reality is somewhat different when you get down to the level of precisions parts used in industrial machinery.
A company that has been designing industry-specific valves for decades likely won’t be manufacturing everything itself internally. It will typically rely on an old-school network of manufacturers which may mean working with a small business consisting of a single expert “craftsman” and a handful of helpers working from a small facility.
“What this means is they’re not doing much in terms of digitization, and it’s difficult to change that because they’re just used to working with pen and paper, basically,” Daedalus founder and CEO Jonas Schneider told TechCrunch. “So you have these very low-tech manufacturers supplying the most critical components for these extremely high-end products.”

Daedalus founder & CEO Jonas Schneider Image Credits: Daedalus
Founded in 2019, Daedalus uses similar off-the-shelf hardware available to any manufacturer, but its special sauce lies in the software it deploys on top to control and optimize the “shop floor” — that is, it automates many of the manual tasks involved in producing a particular part. So a customer will send their CAD (computer aided design) drawings as usual, and Daedalus develops these drawings to a finished part with automation permeating the process.
“It’s about orchestrating all of the workflows across the production, planning and scheduling of those running around on the factory floor doing the work,” Schneider said.
For context, when production begins for a new “part” in a machine, there are typically dozens of steps and hundreds of decisions involved that impact what tooling will be needed, what settings to use to create the precise shape and dimensions of the part, and so on. And this is where Daedalus enters the fray — its software captures the manufacturing decisions data of one “part,” and uses that to guide the decisions around how a similar part is created in the future. So a slightly bigger valve, or a valve with an extra fitting, might be substantively the same as an earlier part, thus Daedalus uses pattern matching to apply that previous knowledge to configure its machines for the new part.
In many ways, Daedalus extends the basic concept of 3D printing, which has been democratizing the manufacturing process for more than a decade. But with machine learning smarts under the hood, it’s taking things to the next level — it’s like 3D printing on steroids.
“The comparison is very apt — as an outsider to this industry in the beginning, to me it seemed like custom manufacturing had [already] been solved with 3D printing. But it mostly comes down to technical limitations of the process,” Schneider said. “With 3D printing, it still means that you need to design a new part specifically so that it can be 3D-printed, and that actually ends up being quite an expensive process. But for the vast majority of the industrial base, it’s not really feasible, and they can’t do 3D printing because it’s not precise enough, or the materials are not strong enough.
You can frame what what we’re doing, in a sense, as taking this idea from 3D printing and applying it to industrial grade, high-end parts.”
The story so far
Prior to Daedalus, Schneider was technical lead at OpenAI where he was instrumental in getting the company’s robotics division off the ground in 2016. Indeed, OpenAI might be better known today for its flagship ChatGPT AI chatbot, but the company also operated a robotics unit which conducted research into things like solving a Rubik’s Cube with a robotic hand, a project that Schneider was directly involved in.
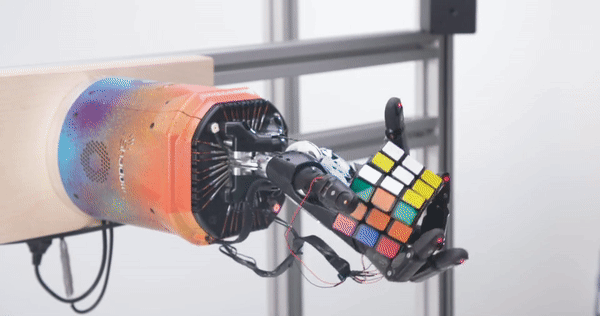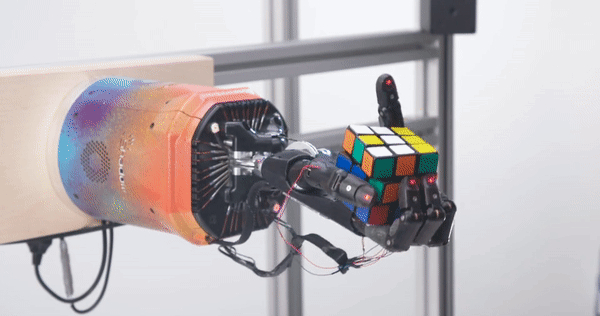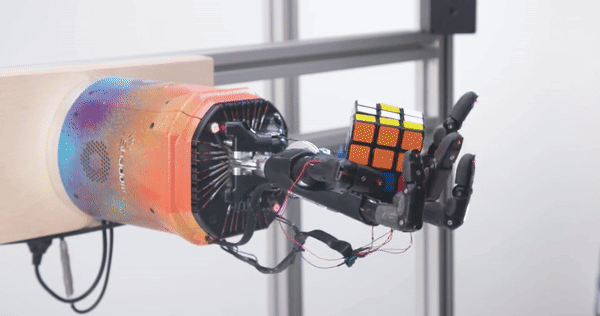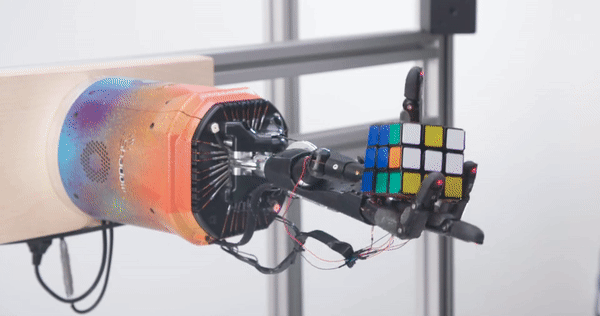
OpenAI’s Rubik’s Cube hand Image Credits: OpenAI
OpenAI ultimately disbanded this team in 2021, but Schneider had spearheaded the software engineering side of operations for more than three years before he departed to start Daedalus in 2019.
While there were various reasons why Schneider ended up leaving to form his own startup, there was one experience he encountered building the Rubik Cube hand which played a bit part in his decision to launch Daedalus.
“At one point, the robot hand broke down and we had to get spare parts,” Schneider said. “And guess what? They needed to be precision manufactured. So there were these machines just like ours today, but we had to wait months to get these parts. And I thought, why is it so hard to get spare parts here? All of this contributed to me looking at this whole manufacturing space a bit more.”
For now, Daedalus has a single 50,000 square-foot factory factory in Karlsruhe from where it largely targets the German-speaking markets including Austria and Switzerland. In the near term, the plan is to expand to a second factory in Germany, and then further afield if demand is sufficient.
“This is the blueprint factory, right? This is where we’re learning all of the systems and all of the knowledge and distilling it into our way of producing these parts,” Schneider said. “And then in the long run, we’ll put these factories wherever our customers need them.”









